What is an RTD sensor

A resistance temperature detector (RTD) sensor is a type of electrical temperature sensor that measures the change in temperature by detecting changes in electrical resistance.
This type of sensor operates on the principle that the material resistance changes when the temperature changes.
But how do I know what is RTD? Common RTD sensors are PT100 or PT1000 sensors, with “PT” standing for platinum and the numbers denoting the resistance of the sensor at 0°C.
RTD sensors offer high accuracy and stability, making them ideal for precise temperature measurements. They have a wide temperature range and a linear response to temperature changes. However, they can be more expensive than other sensors and require a power source for operation.
This article will provide an overview of RTD sensors, including their types, construction, working principles, and applications. So you have a good understanding of this type of sensor and its uses.
The Principle and Theory Behind RTDs
Resistance temperature detectors are built on the principle that as the temperature of a metal changes, so does its resistance, including lead wire resistance. In other words, their electrical resistance increases with an increase in temperature and decreases with a decrease in temperature.
This is because metals have free electrons, which move more freely at higher temperatures, causing a higher degree of collisions and thus increasing the material's resistance.
The specific resistance-temperature relationship varies depending on the metal used in the RTD sensor.
The most common type of RTD is the platinum-based PT100, where "PT" stands for platinum and "100" refers to its 100 ohms resistance at 0°C. Other less commonly used materials include nickel (NTC) and copper (CTD).
Types of Resistance Temperature Detector Sensors
RTD temperature sensors come in two primary types: wire wound and thin film.
Wire Wound RTDs
Wire wound RTDs are constructed by winding a fine metal wire, typically platinum or nickel, around a ceramic or glass core. The number of winds establishes the resistance value of the sensor.
These sensors offer excellent accuracy and stability over time but can be fragile and have a slower response time compared to thin film RTDs.
Thin Film RTDs
Thin film RTDs are built by depositing a thin layer of platinum or other metal on an insulating substrate, such as glass or ceramic. They offer faster response times, higher accuracy, and better stability over time than wire wound RTDs. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture.
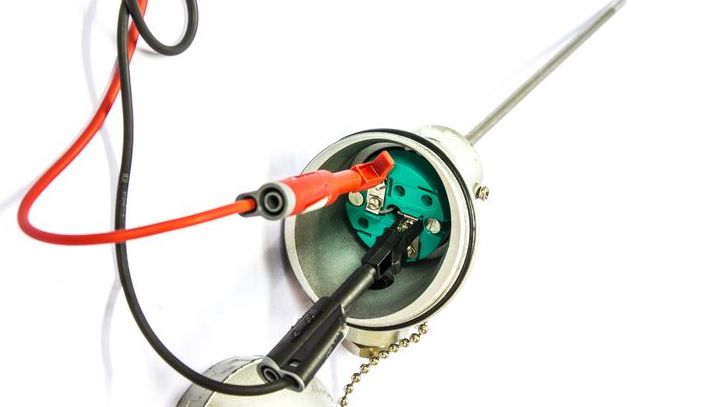

Advantages and Disadvantages of RTD Sensors
RTD sensors offer several advantages over other temperature measurement devices but also have some drawbacks.
Advantages
- High accuracy and stability: RTDs offer highly accurate temperature measurements with low drift over time.
- Wide operating range: They can measure temperatures from −200°C to +850°C, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Linear response: RTD sensors have a linear relationship between resistance and temperature, allowing for easy conversion of readings.
- Good repeatability: They provide consistent results when exposed to the same temperature, making them ideal for calibration purposes.
Disadvantages
- Higher cost: RTD sensors can be more expensive than other types of temperature sensors.
- Fragile construction: Wire wound RTDs can be easily damaged due to their delicate construction.
- Need for a current source: RTDs require a current source for operation, which adds to the overall cost and complexity.
How To Determine The Right RTD?
When choosing an RTD sensor, there are several factors to consider:
Temperature range
When choosing an RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector), it is vital to select one that can accurately measure the temperature range required for your specific application.
This guarantees precise and reliable temperature readings, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of your system.
Temperature Accuracy
When selecting an RTD sensor, the number of wires is another crucial aspect to consider for temperature accuracy.
The level of accuracy needed will vary depending on the specific application. It is essential to choose an RTD sensor with the appropriate number of wires to meet these accuracy requirements and ensure reliable and precise measurements.
Response time
The response time of an RTD sensor is how quickly it can detect a temperature change. This can be critical for certain applications, where quick responses are needed to ensure the safety and efficacy of a system.
Environmental factors
It is essential to consider any environmental factors that may affect the performance of an RTD sensor, such as humidity or vibration levels.
Choosing the right housing and protection for the sensor can ensure its accurate and reliable operation in these conditions
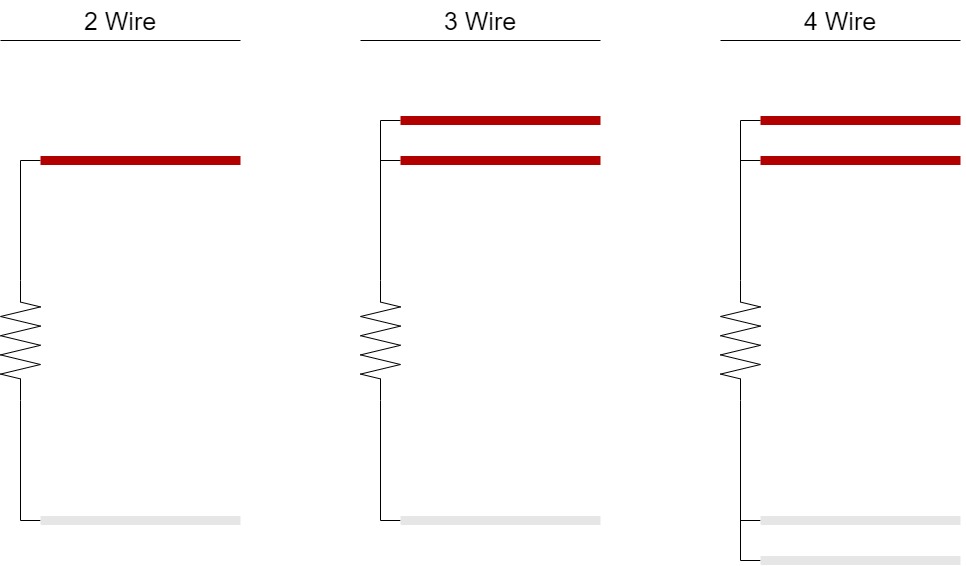
RTD Sensor Wire Configuration and Connection Types
RTDs can be connected in two different configurations: 2-wire or 3-wire. The difference lies in the way the lead wires are connected to the sensor itself.
Two Wire Configuration
In a 2-wire configuration, both lead wires are connected directly to the RTD sensor. Two wires is the simplest wiring method but can introduce lead-wire resistance, which can affect the accuracy of temperature measurements.
Advantages of Two-Wire Configuration
- Simplicity: A two-wire configuration is the simplest electrical connection for RTD sensors, which makes it easy to set up and use. This simplicity also reduces initial costs related to wiring and connectivity.
- Compatibility: It is widely compatible with many different types of instrumentation because of its simplicity, allowing for a range of devices to be easily connected without complex wiring schemes.
Disadvantage of Two-Wire Configuration
- Lead-Wire Resistance Impact: The key disadvantage of a two-wire configuration is that the lead wires’ resistance adds to the measured resistance, which can result in a less accurate temperature reading. This can particularly impact accuracy in applications where the sensor is located far from the reading instrumentation.
Three Wire Configuration
In a 3-wire configuration, one lead wire is connected to one end of the RTD sensor, and the other two lead wires are connected to the opposite end of the resistor. This method compensates for any lead-wire resistance, resulting in more accurate temperature measurements.
Advantages of Three-Wire Configuration
- Compensation for Lead-Wire Resistance: The three-wire configuration significantly reduces the effect of lead-wire resistance on the measurement, enhancing the accuracy of the RTD sensor, especially in circumstances where there is a considerable distance between the sensor and the reading device.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While offering more precision than the two-wire configuration, the three-wire setup is more cost-effective than the four-wire configuration because it requires less wiring material and simpler instrumentation.
Disadvantages of Three-Wire Configuration
- Complexity in Installation: Compared to a two-wire system, the three-wire configuration is more complex, requiring careful setup and calibration to ensure that the lead-wire resistances are properly balanced and do not adversely affect the measurement.
- Potential Inaccuracies: If the lead wires are not exactly the same resistance, it can introduce error, as the three-wire configuration assumes that the resistance in the two leads on the same side of the RTD are identical. If they are not, this can result in inaccuracies in temperature measurement.
Four Wire Configuration
In a 4-wire configuration, two lead wires are used to pass current through the RTD sensor, while the other two lead wires are used to measure the voltage drop across the sensor. This method eliminates any errors caused by lead-wire resistance and offers the most accurate temperature measurements.
Advantages of Four Wire Configuration
- Elimination of Lead-Wire Resistance Impact: A four-wire configuration offers the highest accuracy for RTD measurements by completely eliminating the effect of lead-wire resistance on the measurement, ensuring the most precise temperature readings.
- Stability in Long-Distance Applications: This configuration is ideal for situations where the sensor needs to be placed far from the measurement instrumentation, as it ensures that the distance does not compromise the accuracy of the temperature readings.
Disadvantages of Four Wire Configuration
- Increased Complexity and Cost: The four-wire configuration is more complex regarding wiring and circuitry. This complexity can lead to higher costs for materials and installation.
- More Extensive Calibration Requirements: While offering superior accuracy, this configuration may require more extensive calibration and maintenance to ensure all four wires remain in optimal condition for accurate measurements.

Installation Guidelines for RTD Temperature Sensors
RTDs should be installed carefully to ensure accurate temperature measurements. Here are some installation guidelines:
- To ensure accurate readings, it is important to avoid installing the sensor near heat sources like motors or heaters, as they can introduce unwanted variations.
- When installing the sensor in harsh environments, it is recommended to use a protective sheath. This will provide additional protection and help maintain the sensor's performance and longevity.
- Proper grounding plays a crucial role in reducing noise and interference in the sensor's measurements. Ensuring a solid grounding connection will enhance the accuracy and reliability of the readings.
- When selecting an RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) for your specific application, it is essential to choose the right type that suits your needs. Factors such as temperature range, accuracy requirements, and environmental conditions should be considered to achieve optimal performance and accurate temperature measurements.
Other Things to consider when Choosing a RTD Temperature sensor
Apart from the factors mentioned above, there are a few other things to consider when selecting an RTD sensor:
- Material compatibility: Ensure that the sensor material is compatible with the medium it will be exposed to.
- Environmental conditions: Consider whether the sensor will be used in wet, corrosive, or hazardous environments.
- Cost: The cost of an RTD sensor can vary significantly depending on its type, accuracy, and other features.
- Calibration requirements: Some applications may require periodic calibration of the sensor. Consider this when selecting an RTD.
Where To Buy RTD Temperature Sensor?
RTD sensors can be purchased from various suppliers, including online retailers and industrial supply stores. In our experience, a good choice is Wika which sells all kinds of different resistance temperature detectors.
There you can find different models and technical specifications for each temperature sensor.
For logging temperature measurements we have our software platform SAFE. A test software built to log data from sensors such as RTD sensors. You can download and try it right here.
Conclusion
RTDs are widely used in various industries for their accuracy, stability, and wide operating range. They come in different types, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
When selecting an RTD sensor, consider the temperature range, accuracy requirements, response time, and environmental conditions of your application.
Proper installation and material compatibility are crucial for reliable and accurate temperature measurements.
So make sure to follow the guidelines and choose a reputable supplier when purchasing an RTD sensor. So, go ahead and use this versatile and reliable temperature sensor for your next project or application.